2 Moving average cross EA
Moving average (MA) is a simple technical analysis tool that smooths out price data by creating a constantly updated average price. The average is taken over a specific period, like 10 days, 60 minutes, 20 weeks or any time the trader chooses. There are advantages to using a moving average in your trading, as well as options on what type of moving average to use. Moving average strategies are also popular and can be tailored to any period, suiting both long-term investors and short-term traders. (See also: The Top Four Technical Indicators Trend Traders Need to Know.)
Moving average can also act as support or resistance. In an uptrend, a 50-day, 100-day or 200-day moving average may act as a support level. This is because the average acts like a floor (support), so the price bounces up off it. In a downtrend, a moving average may act as resistance; like a ceiling, the price hits the level and then starts to drop again.
The price will not always “respect” the moving average in this way. The price may run through it slightly or stop and reverse prior to reaching it.
As a general guideline, if the price is above a moving average, the trend is up. If the price is below a moving average, the trend is down. However, moving averages can have different lengths (discussed shortly), so one MA may indicate an uptrend while another MA indicates a downtrend.
Types of Moving Averages
A moving average can be calculated in different ways. A five-day simple moving average (SMA) adds up the five most recent daily closing prices and divides it by five to create a new average each day. Each average is connected to the next, creating the singular flowing line.
Another popular type of moving average is the exponential moving average (EMA). The calculation is more complex, as it applies more weighting to the most recent prices. If you plot a 100-day SMA and a 100-day EMA on the same chart, you’ll notice that the EMA reacts more quickly to price changes than the SMA does, due to the additional weighting on recent price data.
Moving averages are calculated based on historical data, and nothing about the calculation is predictive in nature.
Moving averages work quite well in strong trending conditions but poorly in choppy or ranging conditions. Adjusting the time frame can remedy this problem temporarily, although at some point, these issues are likely to occur regardless of the time frame chosen for the moving average
Trading Strategies – Crossovers 2 Moving average
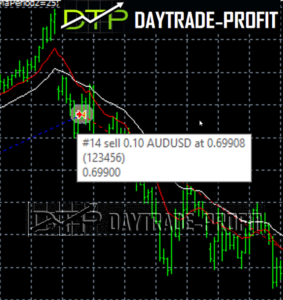
The strategy is to apply two moving averages to a chart: one longer and one shorter. When the shorter-term MA crosses above the longer-term MA, it’s a buy signal, as it indicates that the trend is shifting up.
When the shorter-term MA crosses below the longer-term MA, it’s a sell signal, as it indicates that the trend is shifting down.

Entry strategy
This EA has 2 entry strategies:
1. Break-in (buy order): The EA opens a trade if the short moving average breaks up long moving average

2. Break out (sell order): The EA opens a trade if the short moving average breaks down long moving average